Bliss can be characterized in numerous ways. In brain research, there are two famous ideas of bliss: decadent and eudaimonic. Libertine joy is accomplished through encounters of delight and joy, while eudaimonic joy is accomplished through encounters of importance and reason. The two kinds of joy are reachable and add to generally speaking prosperity in various ways.
Visit here to know more.
Characterize joy
While we know it when we feel it, joy is trying to characterize it. Joy is a positive close to the home state, yet every individual’s insight into that positive profound state is emotional. When and why bliss is capable might be the consequence of various variables cooperating, including society, values, and character attributes.
Given the trouble of coming to an agreement about how satisfaction is characterized, clinicians frequently try not to involve the term in their examination. All things considered, therapists allude to prosperity. While it might ultimately be viewed as inseparable from satisfaction, the idea of prosperity in mental exploration has empowered researchers to the more likely to characterize and quantify it.
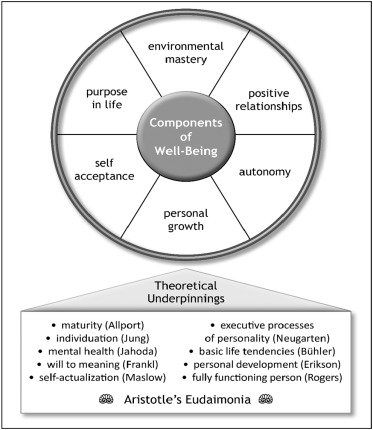
In any case, even here, numerous ideas of well-are being. For instance, Diener and partners characterize emotional prosperity as a mix of positive feelings and how much an individual appreciates and is happy with their life. In the interim, Raif and his associates tested Diner’s decadent viewpoint of emotional prosperity by proposing an elective thought of mental prosperity. As opposed to abstract prosperity, mental prosperity is estimated along six developments connected with self-realization: independence, self-awareness, reason throughout everyday life, self-acknowledgment, authority, and positive associations with others.
Visit here to know more about 15 games like the hollow
Beginning of the idea of decadent bliss
The possibility of pleasurable satisfaction traces all the way back to the fourth century BCE, when a Greek savant, Aristippus, instructed that a definitive objective of life ought to be to boost delight. Over the entire course of time, numerous logicians, including Hobbes and Bentham, have followed this decadent view. Clinicians who concentrate on joy according to a libertine point of view have projected a wide net by conceptualizing hedonia concerning delights of both psyche and body. In this view, delight comprises boosting joy and limiting agony.
In American culture, gluttonous joy is in many cases seen as the ultimate objective. Mainstream society depicts an active, social, euphoric perspective on life, and thus, Americans frequently accept that gratification in its different structures is the most ideal way to accomplish satisfaction.
Beginning of the idea of eudaimonic bliss
Eudaimonic bliss is truly focused on less consideration in American culture in general yet no less significant in the mental examination of satisfaction and prosperity. Like hedonia, the idea of eudaimonia traces all the way back to the fourth century BC, when Aristotle first proposed it in quite a while work, the Nicomachean Ethics. As per Aristotle, to accomplish joy, an individual ought to carry on with an existence as per his characteristics. He asserted that individuals are continually endeavoring to realize their true capacity and be their best, which prompts more prominent reason and importance.
Like the decadent view, numerous savants including Plato, Marcus Aurelius, and Kant fell in line with the eudaimonic point of view. Mental speculations, for example, Maslow’s pecking order of necessities, which highlight self-completion as the most significant standard throughout everyday life, support an eudaimonic view on human satisfaction and thriving.
Research on Hedonic and Eudaimonic Happiness
While a few mental specialists who concentrate on joy come from either a simply gluttonous or an absolutely eudaimonic viewpoint, many concur that the two sorts of bliss are important to boost prosperity. For instance, in an investigation of gluttonous and eudaimonic ways of behaving, Henderson and their partners found that epicurean ways of behaving expanded positive feelings and life fulfillment and directed feelings, while likewise decreasing pessimistic feelings, stress, and melancholy. did. In the meantime, eudaimonic conduct led to a feeling of more prominent significance and rise throughout everyday life or a feeling of passing judgment on moral temperances. This study demonstrates that decadent and eudaimonic ways of behaving add to prosperity in various ways and are thusly both important to boost satisfaction.
Blissful variation
While both eudaimonic and libertine satisfaction seem to work well for a specific reason by and large being, epicurean transformation, otherwise called the “decadent treadmill,” takes note of that, for the most part, individuals have a benchmark of bliss. It happens regardless of what occurs in their life. In this manner, regardless of spikes in satisfaction and delight, when one has a pleasurable encounter, for example, showing up at a party, eating a tasty dinner, or winning an award, the oddity before long wears off and individuals are at their run of the mill levels of bliss. return.
The mental examination has shown that we as a whole have a satisfaction set point. Psychologist Sonya Lyubomirsky has framed the three parts that add to that set point and how much each issue is. As per her computations, half of a singular’s bliss set not set in stone by hereditary qualities. Another 10% is the consequence of conditions that are beyond one’s control, similar to where they’re conceived and who their folks are. At last, 40% of one’s bliss set point is influenced quite a bit by. Consequently, while we can decide that we are so glad to a specific degree, a portion of our still is up in the air of things we can’t change.
Decadent variation is probably going to happen when one participates in momentary joys. This sort of happiness can further develop a state of mind however this is over in a short while. One method for combatting a re-visitation of your satisfaction set point is to participate in more eudaimonic exercises. Significant exercises like taking part in side interests require more prominent ideas and exertion than decadent exercises, which expect almost no effort to appreciate. However, while gluttonous exercises become less powerful at summoning bliss after some time, eudaimonic exercises become more viable.
While this might cause it to seem like the way to bliss is eudaimonia, at times not functional to take part in the exercises that bring out eudaimonic joy. Assuming you’re feeling miserable or pushed, frequently indulging yourself with a basic libertine joy, such as eating treats or standing by listening to the main tune, can be a speedy state of mind promoter that requires significantly less exertion than taking part in a eudaimonic action. Subsequently, both eudaimonia and hedonia play a part to play in one’s general joy and prosperity.